In today’s fast-paced digital world, electronic signatures have become a vital part of doing business. They provide a convenient, secure, and efficient way to sign documents without the need for physical presence. One crucial aspect of electronic signatures that ensures their legality and security is electronic signature certification. This article delves into what electronic signature certification is, why it matters, how it works, and the different types available.
Introduction
Electronic signatures (e-signatures) are increasingly used across various industries to streamline processes, reduce paper usage, and enhance transaction speeds. However, for e-signatures to be trusted and legally binding, they must be certified. Electronic signature certification is the process that validates the authenticity and integrity of an e-signature, ensuring that the signature is genuine and that the document has not been tampered with after signing.
What is Electronic Signature Certification?
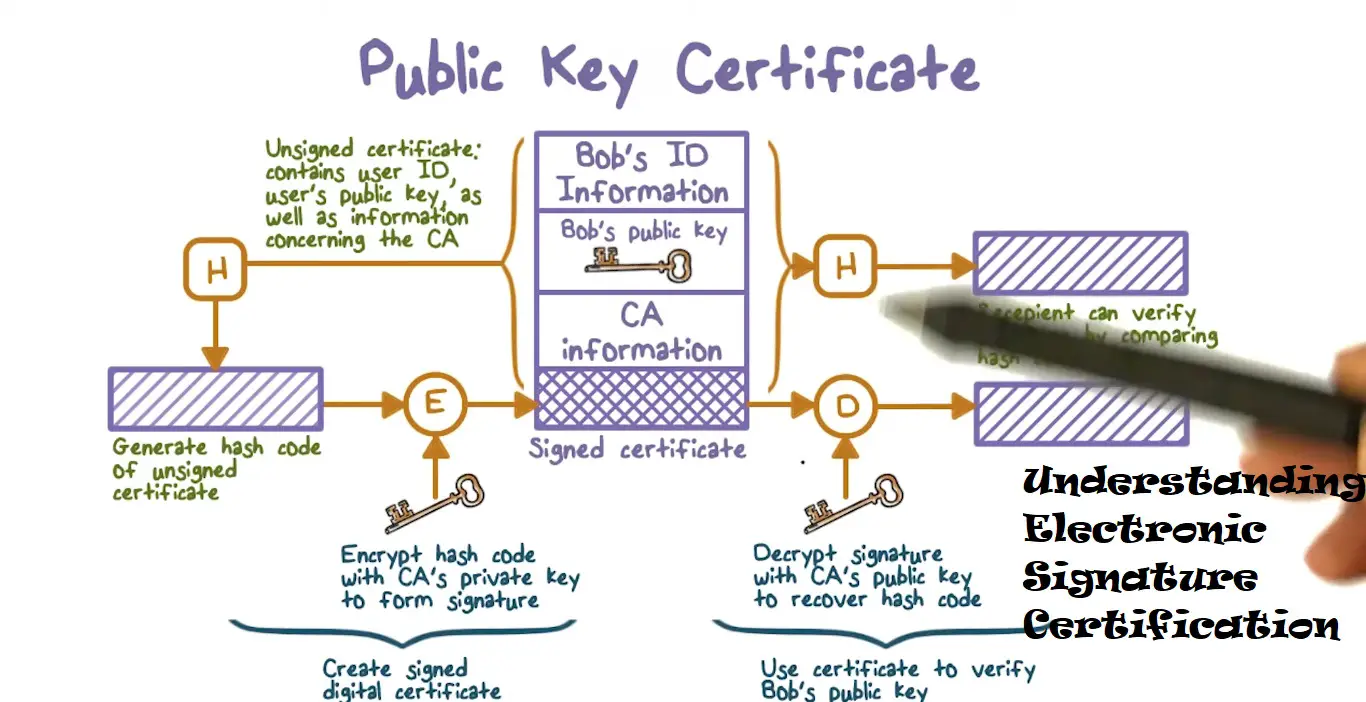
Electronic signature certification involves the use of cryptographic technology to verify the identity of the signer and the integrity of the signed document. This process provides assurance that the e-signature is valid and legally binding. Certification typically involves the issuance of a digital certificate by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA), which acts as a trusted third party to verify the signer’s identity.
Importance of Electronic Signature Certification
- Legal Validity: Certified electronic signatures are recognized as legally binding in many jurisdictions. Certification ensures that the signature meets legal standards and can be used in court if needed.
- Security: Certification adds a layer of security, protecting against fraud and ensuring that the document has not been altered after signing.
- Trust: Certified e-signatures build trust between parties, as they provide assurance that the signatures are authentic and the identities of the signers are verified.
- Compliance: Many industries, especially those dealing with sensitive information, require compliance with specific regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA). Certification helps meet these regulatory requirements.
How Electronic Signature Certification Works
The process of electronic signature certification typically involves the following steps:
- Digital Certificate Issuance: A trusted Certificate Authority (CA) issues a digital certificate to the signer. This certificate includes the signer’s public key and is used to verify their identity.
- Signing Process: When a document is signed electronically, a unique digital signature is created using the signer’s private key and the document’s contents. This signature is then encrypted and appended to the document.
- Verification: To verify the signature, the recipient uses the signer’s public key (included in the digital certificate). The public key decrypts the digital signature, confirming the signer’s identity and ensuring that the document has not been altered since it was signed.
Types of Electronic Signature Certification
There are several types of electronic signature certification, each offering different levels of security and legal validity:
- Simple Electronic Signatures (SES):
- Description: Basic form of e-signatures that are not certified by a CA.
- Use Cases: Suitable for low-risk transactions where security and legal validity are not primary concerns.
- Limitations: Lack of certification means lower security and legal standing.
- Advanced Electronic Signatures (AES):
- Description: E-signatures that are uniquely linked to the signer, capable of identifying the signer, and created using means that the signer can maintain under their sole control.
- Use Cases: Suitable for moderate-risk transactions requiring higher security and legal validity.
- Certification: Often certified by a CA to ensure identity verification and document integrity.
- Qualified Electronic Signatures (QES):
- Description: The highest standard of e-signatures, offering the highest level of security and legal standing. QES are based on a qualified certificate issued by a CA and created using a qualified electronic signature creation device.
- Use Cases: Suitable for high-risk transactions where maximum security and legal validity are essential.
- Certification: Requires a qualified CA and strict adherence to regulatory standards.
Legal Frameworks and Standards
Various legal frameworks and standards govern the use and certification of electronic signatures. Some of the most prominent include:
- eIDAS Regulation (EU):
- Scope: Applies across the European Union.
- Key Provisions: Establishes a common framework for electronic identification and trust services, including electronic signatures, within the EU. Recognizes SES, AES, and QES, with QES having the highest legal standing.
- ESIGN Act (USA):
- Scope: Applies across the United States.
- Key Provisions: Grants electronic signatures the same legal standing as handwritten signatures, provided certain conditions are met.
- UETA (USA):
- Scope: Adopted by most US states.
- Key Provisions: Provides a legal framework for electronic transactions, ensuring that electronic signatures are legally recognized.
- PIPEDA (Canada):
- Scope: Applies across Canada.
- Key Provisions: Governs the use of electronic signatures and ensures their legal recognition.
Implementing Electronic Signature Certification
Implementing electronic signature certification involves several key steps:
- Choose a Trusted CA: Select a reputable Certificate Authority to issue digital certificates. The CA should comply with relevant legal and regulatory standards.
- Integrate E-Signature Solution: Implement an e-signature solution that supports certification. Popular options include DocuSign, Adobe Sign, and HelloSign.
- Educate Users: Ensure that users understand how to use the e-signature solution and the importance of certification.
- Monitor and Audit: Regularly monitor and audit the e-signature process to ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
Best Practices for Using Certified Electronic Signatures
- Verify Identity: Always verify the signer’s identity using a trusted CA before issuing a digital certificate.
- Secure Private Keys: Ensure that private keys used to create digital signatures are securely stored and protected from unauthorized access.
- Use Strong Encryption: Employ strong encryption methods to protect digital signatures and ensure document integrity.
- Regularly Update Software: Keep e-signature software and systems updated to protect against security vulnerabilities.
- Maintain Audit Trails: Keep detailed audit trails of all signed documents to provide proof of signing and support legal compliance.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between an electronic signature and a digital signature? An electronic signature is a broad term that refers to any electronic method of signing a document. A digital signature is a type of electronic signature that uses cryptographic techniques to ensure the authenticity and integrity of the signed document.
2. Are certified electronic signatures legally binding? Yes, certified electronic signatures are legally binding in many jurisdictions, provided they meet the required legal standards and are issued by a trusted CA.
3. How do I choose a Certificate Authority (CA)? Choose a CA that is reputable, complies with relevant legal and regulatory standards, and has a proven track record of issuing reliable digital certificates.
4. Can electronic signatures be used for all types of documents? While electronic signatures can be used for many types of documents, certain documents (e.g., wills, certain real estate transactions) may require handwritten signatures by law. Always check the legal requirements for your specific use case.
5. What should I do if I suspect an electronic signature has been tampered with? If you suspect an electronic signature has been tampered with, immediately contact the CA and review the audit trail provided by the e-signature solution. Legal advice may also be necessary.
Conclusion
Electronic signature certification is a crucial component of the e-signature process, providing the security, legal validity, and trust needed for modern digital transactions. By understanding the different types of electronic signature certification and implementing best practices, businesses and individuals can confidently use e-signatures to streamline workflows and protect sensitive information. As technology continues to evolve, electronic signature certification will remain a key element in ensuring the integrity and authenticity of digital signatures.
