Introduction
Email authentication verifies that an email comes from the claimed source. It helps prevent phishing and spam.

Email authentication is crucial in the digital age to protect users and organizations from malicious activities. It involves methods like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC that authenticate email origins. These protocols ensure that only legitimate emails reach recipients, reducing the risk of phishing and spam.
Effective email authentication enhances email deliverability and safeguards brand reputation. By implementing these protocols, businesses can secure their communication channels and build trust with their audience. Understanding and adopting email authentication practices are essential for maintaining a secure and trustworthy email environment.
The Importance Of Email Authentication
Email authentication is critical for online communication. It verifies that an email is from a trusted source. Without it, emails can be spoofed, leading to various security risks. Understanding email authentication helps protect both senders and recipients.
Risks Of Unauthenticated Emails
- Phishing Attacks: Unauthenticated emails can be used for phishing. Cybercriminals trick users into giving sensitive information.
- Spam: Spam emails often come from unauthenticated sources. These can clutter inboxes and waste time.
- Malware: Unauthenticated emails may contain harmful attachments. Opening these can infect your device with viruses.
- Brand Damage: Fake emails can harm a company’s reputation. Customers may lose trust in the brand.
Benefits Of Secure Email Practices
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Trust | Secure emails build trust with recipients. They know your emails are safe. |
| Reduced Spam | Authenticated emails lower the chance of being marked as spam. This ensures your emails reach the inbox. |
| Enhanced Security | Secure emails protect against phishing and malware. They keep your data safe. |
| Better Deliverability | Authenticated emails have higher deliverability rates. This means more people read your messages. |
Implementing email authentication is essential for secure communication. It protects against various risks and offers many benefits. Make sure your emails are authenticated to build trust and ensure safety.

Credit: www.skysnag.com
Fundamentals Of Email Security
Email security is crucial for protecting sensitive information. It ensures that emails are safe from unauthorized access. Robust email security prevents phishing, spam, and other malicious activities. Understanding the basics of email security helps in safeguarding digital communication.
Key Terms In Email Authentication
Email authentication involves several key terms. These terms are essential for understanding email security:
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): This verifies that the email was not altered.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): This checks if the email comes from an authorized server.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance): This policy tells how to handle unauthenticated emails.
- Encryption: This process converts email content into unreadable text.
How Email Security Works
Email security works through various methods. It involves authentication, encryption, and policies:
- Authentication: The email system checks the sender’s identity. It ensures the email is from a trusted source.
- Encryption: The email content is encrypted. Only the intended recipient can read it.
- Policies: DMARC policies guide how to handle unauthenticated emails. They help in reducing spam and phishing.
The table below summarizes the key components of email security:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| DKIM | Verifies that emails are not altered. |
| SPF | Checks if the email is from an authorized server. |
| DMARC | Guides handling of unauthenticated emails. |
| Encryption | Converts email content into unreadable text. |
Common Email Threats
Email threats are a serious issue. Hackers use them to steal information. Understanding these threats is vital. This section covers common threats to emails.
Phishing Attacks And Their Impact
Phishing attacks trick users. They look like real emails. Hackers steal personal info. This includes passwords and credit card numbers.
The impact of phishing is severe. Users lose money. They also lose trust in email communication. Companies face legal issues. They may lose their reputation.
The Dangers Of Spoofing And Spam
Spoofing is another threat. Hackers send fake emails. These look like they come from trusted sources. Users click on harmful links. Their computers get infected.
Spam emails flood inboxes. They are annoying. They can also carry malware. Users waste time deleting them. Important emails get lost among spam.
Protocols For Email Authentication
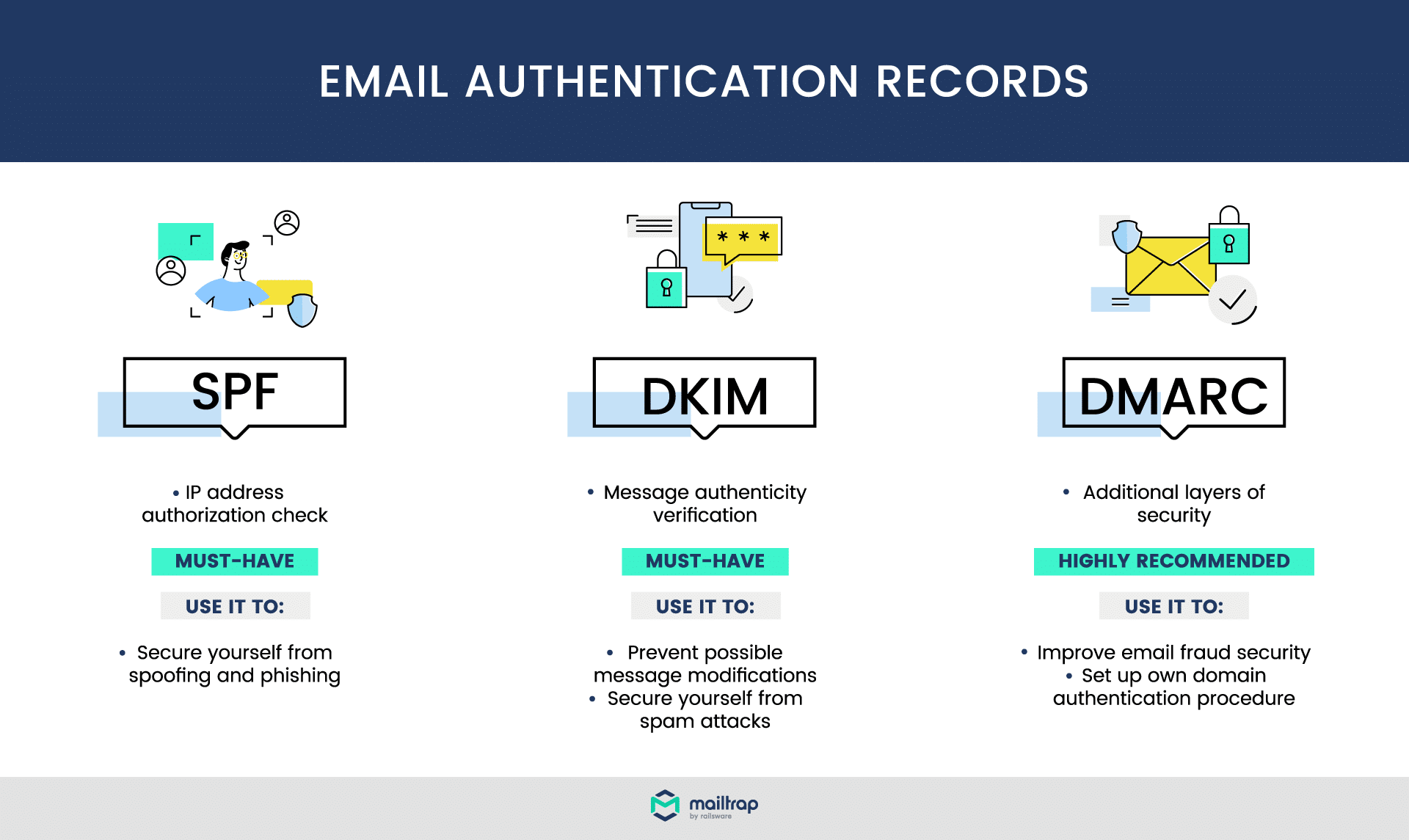
Email authentication is crucial. It helps verify the sender’s identity. This reduces spam and phishing attacks. Three main protocols are used: SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Each plays a unique role in securing email communications.
Spf: Sender Policy Framework Explained
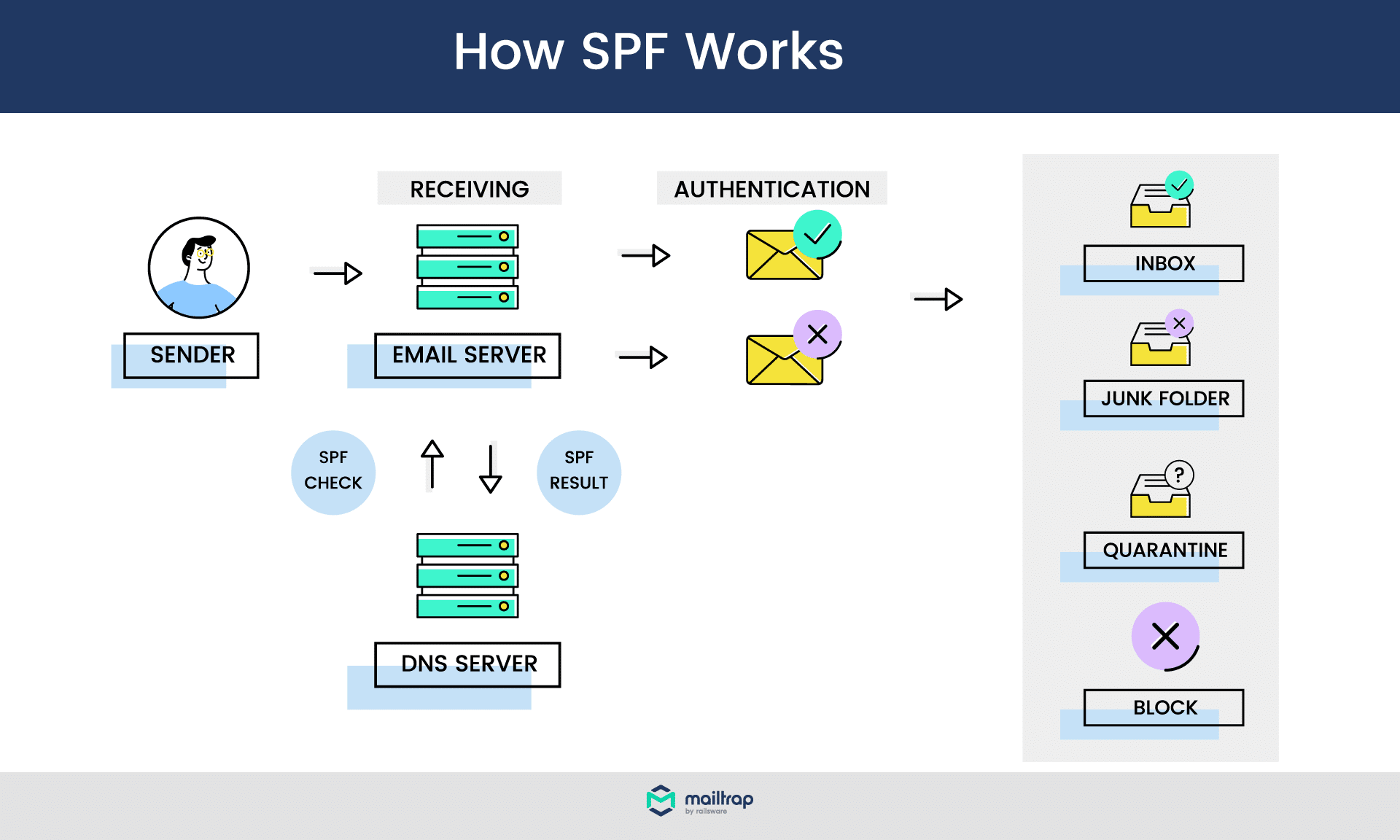
SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework. It allows domain owners to specify which mail servers are allowed to send emails on their behalf. SPF records are added to DNS settings.
Here’s a simple SPF record example:
v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com ~all
This record permits Google’s mail servers to send emails for the domain. If an unauthorized server sends an email, it fails the SPF check.
Benefits of SPF:
- Reduces spam
- Prevents email spoofing
- Improves email deliverability
Dkim: Domainkeys Identified Mail Basics
DKIM stands for DomainKeys Identified Mail. It adds a digital signature to each outgoing email. This signature verifies the email’s origin and integrity.
Key elements of DKIM:
- Public key in DNS records
- Private key on the sending mail server
How DKIM works:
- Email is sent with a DKIM signature
- Receiving server retrieves the public key
- Signature is verified using the public key
Benefits of DKIM:
- Ensures email integrity
- Prevents tampering
- Builds trust with recipients
Dmarc: Domain-based Message Authentication
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. It builds on SPF and DKIM. DMARC policies help domain owners specify how to handle emails that fail authentication.
Key components of DMARC:
- Policy for handling failed emails
- Reporting mechanism
- Alignment with SPF and DKIM
Example of a DMARC record:
v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:[email protected]
This policy rejects emails that fail authentication. It also sends reports to the specified email address.
Benefits of DMARC:
- Improves email security
- Provides detailed reports
- Reduces phishing attacks
Implementing Spf
Email authentication is key for email security. SPF (Sender Policy Framework) helps prevent email spoofing. Implementing SPF ensures that only authorized servers can send emails on your behalf.
Setting Up Spf Records
To set up SPF, you need to add a DNS TXT record. This record specifies which mail servers can send emails from your domain.
- Login to your domain’s DNS management console.
- Find the option to add a new DNS record.
- Select the TXT record type.
- In the ‘Name’ field, enter “@” or your domain name.
- In the ‘Value’ field, enter your SPF rule. A basic rule looks like this:
"v=spf1 include:example.com ~all". - Save the record and wait for DNS propagation.
Best Practices For Spf Configuration
Follow these best practices for effective SPF configuration:
- Use a Neutral Modifier: Use
~allinstead of-allto avoid email delivery issues. - Limit DNS Lookups: Keep the number of DNS lookups under 10 to avoid SPF failures.
- Include Trusted Senders: Use the
includemechanism to add trusted domains. - Regular Updates: Regularly update your SPF records to include new IP addresses or domains.
Proper implementation of SPF enhances email deliverability. It also protects your domain from spoofing attacks.
Setting Up Dkim
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) helps protect your email domain. It verifies the sender’s identity. It also ensures the email content is not altered.
Setting up DKIM is crucial for email authentication. It involves creating DKIM keys and configuring DKIM signatures.
Creating Dkim Keys
DKIM keys are essential for authenticating your emails. They consist of a private key and a public key.
Steps to create DKIM keys:
- Generate a DKIM key pair using a DKIM generator tool.
- Save the private key on your email server.
- Add the public key to your DNS records.
Here is an example of a DNS record for DKIM:
default._domainkey.yourdomain.com IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=public_key"
Configuring Dkim Signatures
Configuring DKIM signatures ensures your emails are signed with your private key.
Steps to configure DKIM signatures:
- Access your email server’s settings.
- Locate the DKIM configuration section.
- Paste the private key generated earlier.
- Enable DKIM signing for outgoing emails.
Here’s a table showing typical email server settings for DKIM:
| Server | Action |
|---|---|
| Gmail | Enable DKIM in Admin Console |
| Office 365 | Enable DKIM in Security & Compliance |
| cPanel | Enable DKIM in Email Authentication |
Once configured, your emails will have a DKIM signature. This signature helps recipients verify the email’s authenticity.
Leveraging Dmarc
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. It helps protect your email domain from unauthorized use. By leveraging DMARC, you can improve your email security. This guide will teach you how to set up and use DMARC effectively.
Crafting A Dmarc Policy
A DMARC policy specifies how your emails should be handled. You need to create a DMARC record in your DNS. This record tells email receivers how to handle emails from your domain. Here are the main steps:
- Identify your domain’s DNS provider.
- Create a DMARC TXT record.
- Set the policy to
none,quarantine, orreject. - Specify the email address for reports.
Below is an example of a DMARC record:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:[email protected]
The p tag defines the policy. rua specifies where to send reports.
Monitoring And Reporting With Dmarc
Monitoring your DMARC reports is crucial. Reports help you see if emails are passing or failing DMARC checks. They also show you where unauthorized use may be happening.
To monitor DMARC, you can use tools like:
- DMARC Analyzer
- Valimail
- DMARCian
These tools help you read and understand DMARC reports. They provide insights into your email security.
Here is a sample DMARC report:
| Domain | Policy | Pass | Fail |
|---|---|---|---|
| yourdomain.com | none | 500 | 20 |
The table shows how many emails passed or failed DMARC.
Additional Email Authentication Measures
Email authentication is a critical aspect of cybersecurity. Beyond basic measures, extra steps can provide more security. These additional measures ensure emails are secure and authentic. Two important ones are TLS and MFA.
Using Tls For Email Encryption
Transport Layer Security (TLS) is a protocol for email encryption. TLS encrypts the data between email servers. This keeps email content safe from hackers. Without TLS, emails can be read by anyone intercepting them.
Implementing TLS is straightforward. Most email providers support it. Check your email settings to enable TLS. Always use the latest version for better security.
The Role Of Mfa In Email Security
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds another layer of security. It requires more than one form of verification. This could be a password and a code sent to your phone.
- MFA makes it harder for hackers to access your email.
- Even if they have your password, they need a second factor.
Setting up MFA is simple. Most email providers offer it. Enable MFA in your account settings. Choose a method that works best for you, like SMS codes or an authentication app.
Regular Maintenance And Monitoring
Regular maintenance and monitoring of email authentication are crucial. This ensures the security and reliability of your email communications. Effective email authentication reduces the risk of phishing and spoofing attacks.
Auditing Email Security
Regularly audit your email security settings. This helps identify any weaknesses. An audit involves checking your SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. Ensure they are correctly configured and up-to-date.
Use the table below to help with your audit:
| Authentication Method | Current Status | Action Required |
|---|---|---|
| SPF | Enabled | Review and update IP addresses |
| DKIM | Enabled | Check key rotation |
| DMARC | Enabled | Review policy and reports |
Updating Authentication Methods
Keep your email authentication methods updated. This ensures they remain effective against new threats. Update your SPF records as your IP addresses change. Rotate your DKIM keys regularly to maintain security.
Here are some steps to follow:
- Review your SPF records quarterly.
- Rotate your DKIM keys every six months.
- Analyze DMARC reports monthly.
Regular updates and monitoring help maintain robust email security. This protects your organization from potential threats.

Future Of Email Authentication
The future of email authentication is bright. New technologies are making emails safer. This helps protect users from scams and phishing. It ensures that only trusted sources can send emails.
Emerging Technologies In Email Security
Many new technologies are improving email security. These include:
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance): This technology helps prevent email spoofing. It lets domain owners protect their email from abuse.
- BIMI (Brand Indicators for Message Identification): BIMI displays brand logos in emails. This helps users identify trusted emails quickly.
- MTA-STS (Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security): MTA-STS ensures emails are sent over secure connections. This prevents eavesdropping and tampering.
Staying Ahead Of Email Threats
To stay ahead of email threats, you must use the latest tools. Here are some tips:
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): This adds an extra layer of security. It requires users to verify their identity in multiple ways.
- Regularly Update Your Systems: Always keep your email systems updated. This helps protect against new threats.
- Educate Your Users: Teach users about email threats. Inform them how to spot phishing emails and other scams.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Do I Authenticate My Email?
Authenticate your email by enabling SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Verify settings in your email service provider’s documentation.
What Is An Email Authentication Method?
An email authentication method verifies the sender’s identity to prevent spam and phishing. Common methods include SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
How Do I Verify Email Authentication?
Verify email authentication by checking SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. Use online tools or your email provider’s settings. Confirm proper configuration to ensure emails are not flagged as spam.
How Do I Fix Email Authentication?
To fix email authentication, configure SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. Update DNS settings and ensure correct alignment. Use email authentication tools for verification.
Conclusion
Email authentication is crucial for maintaining the security and integrity of your communications. Implementing authentication methods helps protect against phishing and fraud. By securing your emails, you can enhance trust and credibility with your recipients. Stay proactive in adopting these measures to ensure a safer digital environment for all.