
DNS Email Records, or DNS MX (Mail Exchange) records, direct email to the correct mail server. They ensure proper email delivery.
DNS Email Records are crucial for routing emails to their intended recipients. These records specify the mail servers responsible for receiving email on behalf of a domain. Each domain must have at least one MX record to function correctly. The priority value in these records determines the order in which mail servers are used.
Lower values signify higher priority. Proper configuration of DNS Email Records is essential for uninterrupted email service. Misconfigured records can lead to email delivery issues. Regularly updating and maintaining these records helps ensure seamless email communication. Understanding DNS Email Records is vital for any domain administrator or IT professional.
Introduction To DNS Email Records
Email communication is essential in today’s digital world. DNS email records ensure email delivery. These records direct emails to the right server. Understanding them helps maintain smooth email operations.
The Role Of DNS in Email Delivery
DNS, or Domain Name System, translates domain names into IP addresses. It ensures emails reach their intended recipients. DNS email records are crucial for this process. They guide email servers to the correct destination.
| DNS Record | Purpose |
|---|---|
| MX Record | Directs email to mail servers. |
| SPF Record | Prevents email spoofing. |
| DKIM Record | Ensures email integrity. |
| DMARC Record | Protects against phishing. |
Key Types Of Email-related DNS Records
There are several key DNS records related to email. Each serves a unique purpose. Below are the main types:
- MX (Mail Exchanger) Records: Directs emails to the correct server.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework) Records: Identifies allowed email servers.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) Records: Provides email authentication.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance) Records: Helps reduce email fraud.
MX records are the most critical. They ensure emails reach the right mail server. SPF records protect against spam. DKIM records verify the sender’s identity. DMARC records enforce SPF and DKIM policies.
Managing these records is vital. It ensures email security and delivery. Ensure they are correctly configured. Regularly update them to stay secure.
Mx Records: Gatekeepers Of Email Routing
MX records are essential for email delivery. They tell email servers where to send your emails. Without MX records, emails would not reach their destination.
Structure Of Mx Records
MX records consist of two main parts: priority and mail server.
- Priority: This is a number. It tells the order of preference for mail servers.
- Mail Server: This is the domain name of the mail server.
Here is an example of an MX record:
10 mail.example.comThe number 10 is the priority. The mail server is mail.example.com. Lower numbers have higher priority.
How Mx Records Affect Email Flow
MX records guide emails to the correct mail servers. They ensure emails are delivered to the right place.
- The sender’s email server checks the recipient’s MX records.
- It identifies the mail server with the highest priority.
- It sends the email to that mail server.
- If the highest priority server is down, it tries the next one.
This process ensures email delivery even if some servers are down.
MX records are crucial for efficient email routing. They help ensure your emails reach their intended recipients.
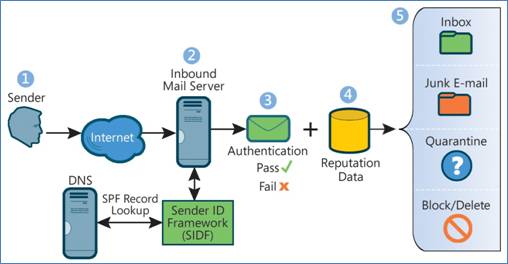
Spf Records: Combating Email Spoofing
Email spoofing is a common problem in today’s digital world. Spammers often send emails that look like they are from trusted sources. This confuses and can lead to security breaches. An SPF record helps to combat this issue.
SPF, or Sender Policy Framework, is a type of DNS record. It tells email servers which IP addresses are allowed to send emails from your domain. By setting up an SPF record, you can reduce the chances of email spoofing.
Spf Record Syntax
An SPF record is a type of TXT record in DNS. It follows a specific syntax to ensure proper validation. Here is an example:
v=spf1 ip4:192.0.2.0/24 ip4:198.51.100.123 a -allEach part of the SPF record has a specific meaning:
- v=spf1: Specifies the SPF version.
- ip4: IP addresses allowed to send emails.
- a: Authorizes the domain’s A record IP address.
- -all: Denies all other IP addresses.
Benefits Of Implementing Spf
Implementing SPF records offers several benefits:
- Reduces Email Spoofing: SPF prevents unauthorized IPs from sending emails from your domain.
- Improves Email Deliverability: Legitimate emails are less likely to be marked as spam.
- Enhances Domain Reputation: Your domain is trusted more by email servers.
An SPF record is a simple yet effective way to secure your email. It adds a layer of protection against phishing and spoofing attacks.
Dkim Records: Ensuring Email Integrity
DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) is a system to protect email integrity. It helps verify that an email comes from a trusted source. This reduces the risk of email spoofing and phishing. DKIM adds a digital signature to each outgoing email. This signature is unique to your domain. It ensures the email was not altered during transit.
Understanding Dkim Signatures
DKIM signatures are like digital fingerprints. They are added to each email you send. These signatures are placed in the email header. The recipient’s email server checks the signature. This server uses your public key to verify the email.
DKIM signatures help in two ways:
- They ensure the email content is not altered.
- They confirm the email’s sender is legitimate.
To understand better, here’s a simple table:
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Signature | Ensures email integrity |
| Public Key | Verifies sender |
Configuring Dkim For Your Domain
Configuring DKIM involves a few steps. First, generate your public and private keys. The private key stays secure on your server. The public key goes into your DNS records.
Follow these steps to configure DKIM:
- Generate DKIM keys using a tool or service.
- Add the public key to your DNS as a TXT record.
- Update your mail server to sign outgoing emails.
- Test your setup using email verification tools.
Here’s an example of a DKIM TXT record:
example._domainkey IN TXT "v=DKIM1; k=rsa; p=yourPublicKeyHere"
Replace “yourPublicKeyHere” with your actual public key. This record tells other servers how to verify your emails.
Dmarc: Linking Spf And Dkim
DMARC stands for Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance. It is an email security protocol. DMARC links SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). This ensures emails are legitimate and not spoofed. DMARC helps in preventing email phishing and spam.
How Dmarc Works
DMARC works by checking SPF and DKIM records. It ensures the email is valid.
Here is a simple process of how DMARC works:
- First, the sender sends an email.
- The receiving server checks the SPF record.
- The receiving server checks the DKIM signature.
- DMARC policy checks the alignment of SPF and DKIM.
- If they align, the email is delivered.
- If not, the email is rejected or marked as spam.
Creating A Dmarc Policy
Creating a DMARC policy is easy. It involves adding a DNS record.
Here is how to create a DMARC policy:
- Log into your DNS management console.
- Add a new TXT record.
- Set the name to “_dmarc.yourdomain.com”.
- Set the value to your DMARC policy.
An example of a DMARC policy is:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:[email protected]This policy allows you to monitor your email traffic.
Once you are confident, you can change the policy to “quarantine” or “reject”.
Verifying Your Email DNS Records
Ensuring your email DNS records are correct is essential. It helps in delivering your emails successfully. Incorrect DNS records can lead to email delivery failures. Verifying these records ensures your emails reach the inbox.
Tools For DNS Record Verification
Several tools can help verify your email DNS records. These tools check if your records are set up correctly. Here are some popular options:
- MXToolbox: A comprehensive tool for DNS checks.
- DNSChecker: Checks DNS records globally.
- Google Admin Toolbox: Ideal for Google Workspace users.
Using these tools is simple. Enter your domain name and initiate the check. The tool will display your DNS records. Verify that the records match your email provider’s settings.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even with proper setup, issues can arise. Here are common problems and solutions:
| Issue | Solution |
|---|---|
| MX Records Missing | Ensure MX records are added. |
| SPF Record Incorrect | Update SPF record as per provider’s guidelines. |
| DKIM Not Set Up | Generate and add DKIM record. |
Always verify changes after updating DNS records. This ensures the issues are resolved. Regular checks prevent future problems.
Best Practices For Email DNS Management
Effective Email DNS management ensures reliable email delivery and security. Follow these best practices to optimize your email DNS setup.
Regular Record Updates
Updating your DNS records regularly keeps your email system secure. Outdated records can lead to delivery issues and vulnerabilities.
Ensure you update the following records frequently:
- SPF Records: Specify authorized mail servers.
- DKIM Records: Add cryptographic signatures to emails.
- DMARC Records: Set policies for handling suspicious emails.
Regular checks ensure your records are current and valid.
Monitoring And Reporting
Monitoring your DNS records helps detect potential issues early. Use tools to track the health of your DNS records.
Set up email alerts for any changes or issues. This allows for quick responses to potential problems.
| Tool | Function |
|---|---|
| MX Toolbox | Monitors MX, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC records. |
| DNSstuff | Provides DNS and network troubleshooting tools. |
Regular reporting ensures you maintain a secure email environment.
Impact Of DNS Records On Email Deliverability
DNS records play a crucial role in email deliverability. Proper DNS configuration ensures emails reach the inbox. Misconfigured DNS records can lead to blacklisting and poor inbox placement.
Understanding Email Blacklisting
Blacklisting happens when email servers mark your emails as spam. This results from sending too many emails or having improper DNS records.
- Spam filters check DNS records.
- Incorrect records raise red flags.
- Servers may block your emails.
DNS records like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC help prevent blacklisting. These records verify the sender’s identity. They ensure your emails are legitimate.
| DNS Record | Purpose |
|---|---|
| SPF | Specifies allowed email servers |
| DKIM | Verifies email content |
| DMARC | Monitors and enforces email policies |
Improving Inbox Placement Rates
Proper DNS records improve inbox placement rates. They show that your emails are safe.
- Set up SPF to list authorized servers.
- Use DKIM to sign emails with a digital signature.
- Implement DMARC to monitor and enforce policies.
Always keep your DNS records up-to-date. Regular checks ensure no issues. Proper DNS records mean better email deliverability.
Advanced Tips For Email Deliverability
Email deliverability can be tricky. Ensuring emails reach the inbox is essential. Many factors influence this. Here, we discuss advanced tips to improve email deliverability.
Leveraging Email Authentication Results
Email authentication is crucial. It helps verify the sender’s identity. Common methods include SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. These tools ensure the email isn’t spam.
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework): Defines which IP addresses can send emails for your domain.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail): Adds a digital signature to your emails.
- DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance): Ensures SPF and DKIM align and provides feedback reports.
Regularly review your authentication results. Adjust policies based on these results. This helps maintain a good sender reputation.
Staying Up-to-date With Email Security Standards
Email security standards evolve. Staying current is vital. Implementing the latest standards improves deliverability.
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| MTA-STS (Mail Transfer Agent Strict Transport Security) | Ensures emails are sent over a secure connection. |
| DANE (DNS-based Authentication of Named Entities) | Uses DNS records to verify email servers. |
Ensure your email servers comply with these standards. Regular updates protect against new threats. This also boosts your email deliverability.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Email Reputation
Ensuring your DNS email records are correct is vital. It helps maintain your email reputation. This affects how others view your emails. A bad email reputation can lead to your emails being marked as spam. This can hurt your business and your communication. Proper DNS email record management is key to avoiding this.
The Continuous Importance Of DNS in Email Security
DNS email records like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC are crucial. They ensure your emails are not spoofed. Spoofing can lead to phishing attacks. These attacks can harm your recipients. They can also hurt your email reputation. Regularly update and check your DNS records. This helps in maintaining email security.
Final Checklist For DNS Email Record Optimization
- Ensure SPF records include all sending sources.
- Enable DKIM for email authentication.
- Set up DMARC to monitor email activities.
- Regularly check DNS records for errors.
- Update DNS records to include new email services.
| DNS Record Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| SPF | Identifies allowed email servers. |
| DKIM | Ensures email content is not altered. |
| DMARC | Monitors and reports email activities. |
Following these steps helps protect your email reputation. Regular maintenance of DNS records is essential. This keeps your emails secure and trusted.
Credit: www.rackaid.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What DNS Records For Email?
DNS records for email include MX, SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. MX routes emails. SPF verifies the sender’s IP. DKIM ensures email integrity. DMARC protects against spoofing.
What Is a DNS Server In Email?
A DNS server in email translates domain names into IP addresses. It helps route emails to the correct mail server.
Does DNS A Record Affect Email?
No, a DNS A Record does not directly affect email delivery. Email relies on MX Records.
What Is The Cname For Email?
A CNAME for email points to a mail server’s domain. It helps direct email traffic correctly.
Conclusion
Understanding DNS email records is crucial for effective email management. They ensure proper email delivery and enhance security. Regularly updating and monitoring these records can prevent issues. Empower your email system with accurate DNS records to maintain seamless communication. Stay informed and proactive for optimal email performance.
