The best time to send cold emails is on Tuesday or Thursday mornings. Aim for 8-10 AM to maximize open rates.
Timing is crucial for the success of cold email campaigns. Sending emails at the right time can significantly improve open and response rates. Research indicates that Tuesdays and Thursdays are the most effective days for cold emailing. Early morning, specifically between 8-10 AM, is ideal as recipients are likely to check their inboxes first thing.
Avoid sending emails on Mondays and Fridays when inboxes are typically flooded or when people are winding down for the weekend. By targeting optimal days and times, you can enhance engagement and achieve better results with your cold email outreach.
Credit: www.siegemedia.com
Introduction To Cold Emailing
Cold emailing is a powerful marketing tool. It helps you reach new prospects. It can open doors to new opportunities. But, it must be done right to be effective. Timing plays a crucial role. Sending emails at the right time can increase engagement. Let’s explore the importance of timing and how to maximize open rates.
The Importance Of Timing
Timing is key in cold emailing. Sending emails at the wrong time can lead to low open rates. People are busy and may ignore your email if sent at a bad time. Knowing the right time to send emails can boost your chances. It ensures your email gets noticed and read.
Maximizing Open Rates
To maximize open rates, understand your audience. Learn their habits and preferences. Test different times to see what works best. Here are some tips to consider:
- Weekdays: Send emails during weekdays, not weekends.
- Morning Hours: Early morning is a good time.
- Lunch Break: Consider sending emails around lunch time.
- Follow-Up: Send follow-up emails if no response.
| Day | Best Time |
|---|---|
| Monday | 8 AM – 10 AM |
| Tuesday | 9 AM – 11 AM |
| Wednesday | 10 AM – 12 PM |
| Thursday | 11 AM – 1 PM |
| Friday | 12 PM – 2 PM |
Analyzing The Audience
Sending cold emails at the right time is crucial. Understanding your audience ensures your emails are read and not ignored. In this section, we will look at how to analyze your audience effectively.
Identifying The Target Demographics
Knowing who your audience is helps in crafting the right message. Identify the age, gender, and interests of your audience.
- Age: Are they young adults, middle-aged, or seniors?
- Gender: Is your audience primarily male, female, or mixed?
- Interests: What are their hobbies or professional interests?
Use surveys or social media insights to gather this information. Knowing these details helps you tailor your email content.
Understanding Recipient Time Zones
Sending emails at the right time increases open rates. Understand the time zones of your audience.
| Region | Time Zone |
|---|---|
| North America | EST, CST, MST, PST |
| Europe | GMT, CET, EET |
| Asia | IST, CST, JST |
Use tools like Google Calendar to convert time zones. This ensures your email reaches the inbox at the best time.
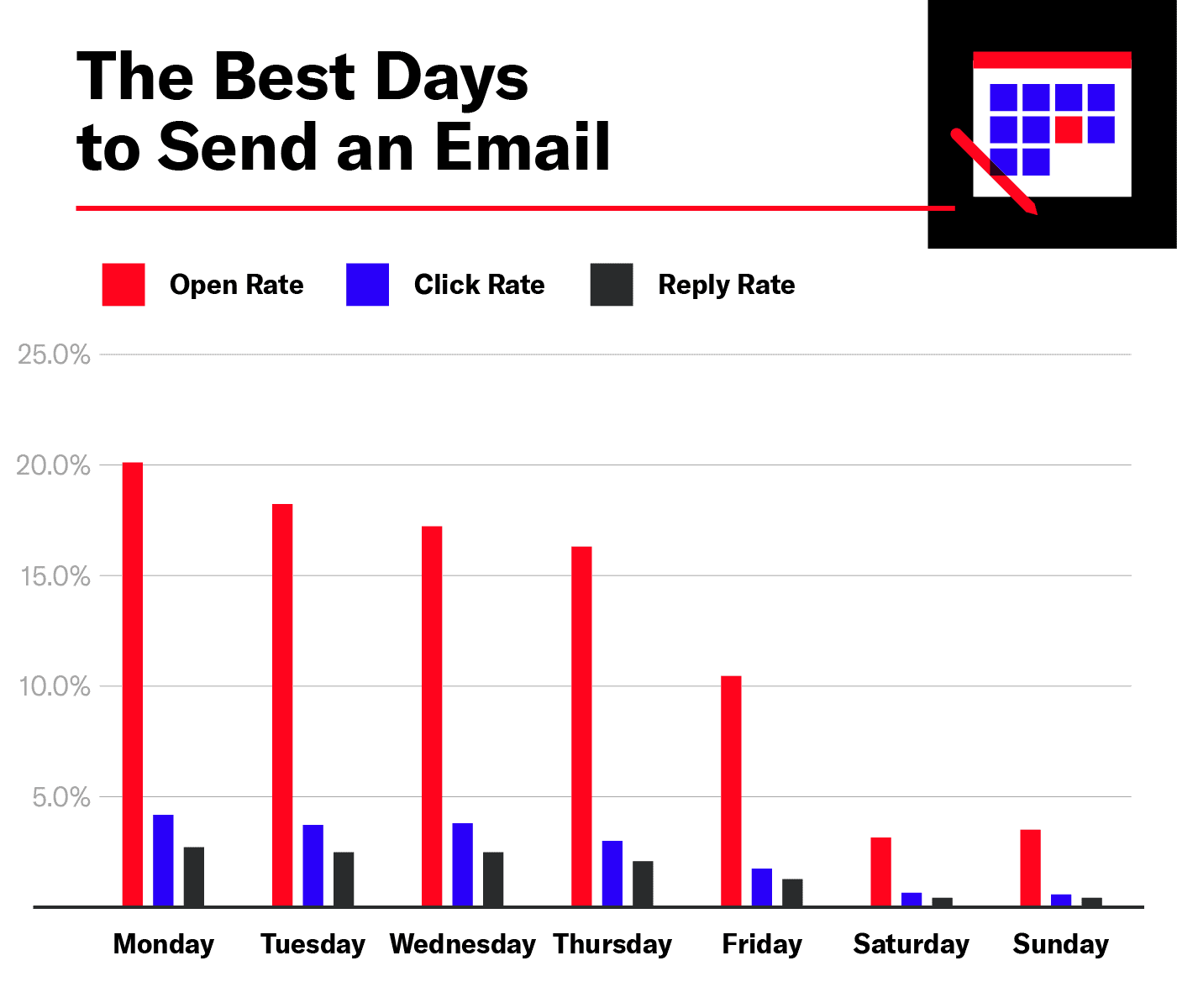
Days Of The Week Matter
Sending cold emails at the right time can boost your response rate. Different days of the week perform differently. Understanding this can help you plan better. Let’s dive into the details.
Midweek Performance Insights
Midweek days, particularly Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday, show high engagement. These days are great for sending cold emails.
On Monday, people catch up on tasks. On Friday, they prepare for the weekend. So, midweek becomes the best time for cold emails.
| Day | Engagement Level |
|---|---|
| Monday | Low |
| Tuesday | High |
| Wednesday | High |
| Thursday | High |
| Friday | Medium |
| Saturday | Low |
| Sunday | Low |
Weekend Versus Weekday Engagement
Weekdays generally outperform weekends in cold email engagement. People often ignore work emails during weekends. They relax and spend time with family.
On weekdays, people are in work mode. They check emails more frequently. This makes weekdays perfect for cold emails.
- Weekdays: Higher engagement.
- Weekends: Lower engagement.
For better results, send your cold emails between Tuesday and Thursday. Avoid weekends for important outreach.
Credit: www.siegemedia.com
Breaking Down The Best Hours
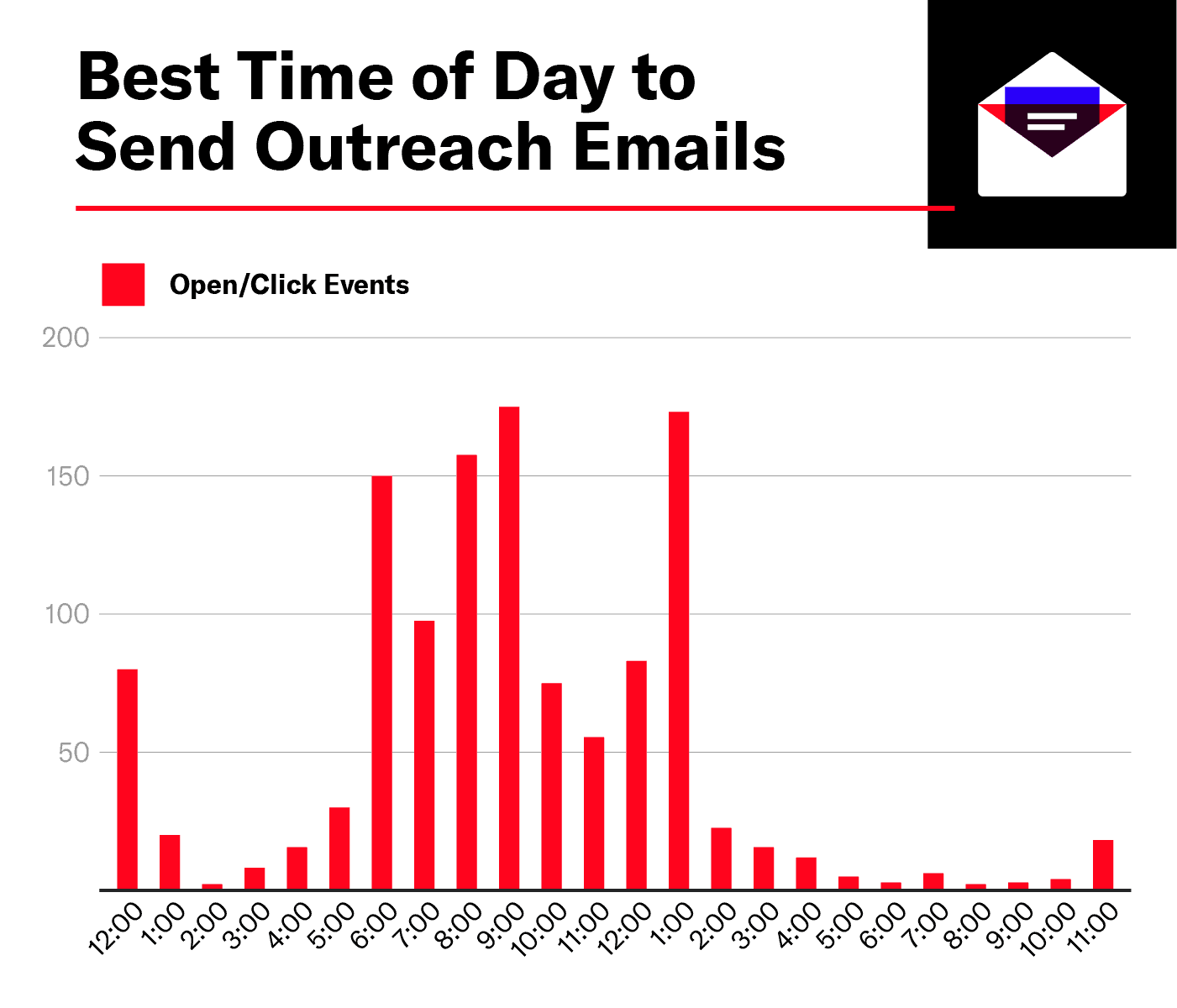
Timing can make or break your cold email strategy. Knowing the best hours to send cold emails helps increase open rates and engagement. This section will guide you through the most effective times of the day.
Morning Momentum
Sending emails in the morning sets the stage for success. The optimal window is between 8 AM to 10 AM. People start their day by checking emails. A morning email can capture their attention quickly.
- Between 8 AM to 10 AM
- High open rates
- Less competition
Afternoon Attention
Afternoons are ideal for detailed reading. Aim to send emails between 1 PM and 3 PM. People often check emails after lunch. They have more time to read and respond.
- Between 1 PM to 3 PM
- People are more relaxed
- Higher engagement
Evening Engagement
Evening emails can catch a relaxed audience. The best time is between 6 PM and 8 PM. People check emails after work. Evening emails often get higher response rates.
- Between 6 PM to 8 PM
- High response rates
- Less email traffic
Here’s a quick summary in table form:
| Time of Day | Best Hours | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Morning Momentum | 8 AM – 10 AM | High open rates, less competition |
| Afternoon Attention | 1 PM – 3 PM | People are relaxed, higher engagement |
| Evening Engagement | 6 PM – 8 PM | High response rates, less email traffic |
The Role Of Industry
Sending cold emails at the right time can boost response rates. The best time to send emails often depends on the industry. Different industries have unique patterns and schedules.
B2b Timing Nuances
B2B stands for Business to Business. Timing is crucial in B2B emails. Business professionals often check emails during work hours. The best days are Tuesday, Wednesday, and Thursday. Aim for mid-morning, around 10 AM, or early afternoon, around 2 PM.
| Day | Best Time |
|---|---|
| Tuesday | 10 AM or 2 PM |
| Wednesday | 10 AM or 2 PM |
| Thursday | 10 AM or 2 PM |
These times work because professionals are less busy. Avoid Mondays and Fridays. People are either catching up or winding down.
B2c Email Strategies
B2C stands for Business to Consumer. Timing here is different from B2B. Consumers often check emails outside work hours. Evenings and weekends are best.
- Weekdays: 8 PM to 10 PM
- Saturday: Morning or late evening
- Sunday: Afternoon or evening
Consumers are relaxed and have more free time. This increases the chance of them reading your email. Tailor your email strategy to fit these times.

Credit: www.klenty.com
Seasonality And Email Success
Understanding the right time to send cold emails can boost your success. Various factors influence this, including seasonality. Different times of the year can impact the effectiveness of your emails. This section explores how holiday seasons and quarterly business cycles affect your cold email strategy.
Holiday Seasons Impact
Holiday seasons can significantly impact email success rates. During holidays, people often take time off work. They might not check their emails as frequently. This can lead to lower open and response rates.
To navigate this, avoid sending cold emails during major holidays. Here is a table showing some holidays to avoid:
| Holiday | Date |
|---|---|
| Christmas | December 25 |
| New Year’s Day | January 1 |
| Thanksgiving | Fourth Thursday of November |
Instead, send emails before or after these dates. This ensures your email is seen when people return to work.
Quarterly Business Cycles
Businesses often operate on quarterly cycles. Understanding these cycles can help you time your emails better. For example, many companies plan budgets and projects at the start of each quarter.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Q1 (January – March): Companies set new goals and budgets.
- Q2 (April – June): Projects are in full swing.
- Q3 (July – September): Mid-year reviews and adjustments occur.
- Q4 (October – December): Companies wrap up the year and plan for the next.
Sending emails at the start of a quarter can be effective. This is when companies are open to new ideas and solutions.
In contrast, avoid sending emails at the end of a quarter. Companies might be focused on closing out their tasks and might not respond.
Use this knowledge to align your cold email strategy with business cycles. This increases the chances of your email being read and responded to.
Technological Tools For Timing
Timing is crucial for cold emails. Using the right tools can increase your success. Technology helps you send emails at the best times. This section explores tools that can help you.
Email Scheduling Software
Email scheduling software helps you send emails at the perfect time. It automates the sending process. You choose the time and the software sends the email. Many tools offer this feature.
- Mailchimp: Schedule emails to reach inboxes at the right time.
- Sendinblue: Use the “Send Time Optimization” feature.
- HubSpot: Schedule emails based on contact’s time zone.
Analytics And Optimization
Analytics tools help you understand when emails are most effective. They track open rates and responses. This data helps you optimize your email timing.
Here are some useful tools:
- Google Analytics: Track website traffic from your emails.
- Mixpanel: Analyze user engagement and interaction.
- Crazy Egg: Visualize where users click after opening your email.
Using these tools, you can improve your email strategy. This leads to higher engagement and better results.
| Tool | Feature |
|---|---|
| Mailchimp | Schedule Emails |
| Sendinblue | Send Time Optimization |
| HubSpot | Time Zone Scheduling |
| Google Analytics | Track Website Traffic |
| Mixpanel | Analyze Engagement |
| Crazy Egg | Visual Click Maps |
Crafting The Perfect Follow-up
Following up on a cold email can be challenging. You want to remain top-of-mind without being intrusive. The key is to strike a balance between persistence and respect for the recipient’s time. This section will guide you through the best practices for crafting the perfect follow-up email.
Timing Your Sequences
Timing is crucial in follow-up emails. Sending too soon may seem pushy. Waiting too long may result in your email being forgotten. A well-timed follow-up can boost your chances of a response.
- First Follow-Up: Send it 3 days after the initial email.
- Second Follow-Up: Send it 5 days after the first follow-up.
- Third Follow-Up: Send it 7 days after the second follow-up.
Follow this sequence to stay on their radar without being annoying. Always be mindful of weekends and holidays.
Persistence Without Annoyance
Your persistence should never cross into annoyance. Each follow-up should add value.
- Personalize: Reference their interests or recent activities.
- Offer Value: Share a useful resource or piece of information.
- Keep it Short: Write concise, straightforward follow-ups.
Use these strategies to maintain a positive tone. Always give an easy opt-out option.
| Follow-Up Timing | Action |
|---|---|
| 3 Days After Initial Email | Send First Follow-Up |
| 5 Days After First Follow-Up | Send Second Follow-Up |
| 7 Days After Second Follow-Up | Send Third Follow-Up |
Remember, persistence is key, but always be respectful. With the right timing and approach, you can craft the perfect follow-up emails that get responses.
Case Studies And Success Stories
Knowing the best time to send a cold email can boost your outreach. Many companies have tested different times and shared their results. Learning from their experiences can help you find the perfect time to hit send.
Learning From The Best
Successful companies have shared their winning strategies. Here are some examples:
| Company | Best Time to Send | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Company A | Tuesday, 10 AM | 45% |
| Company B | Wednesday, 9 AM | 50% |
| Company C | Thursday, 2 PM | 55% |
These companies found that mid-week mornings or early afternoons work best. These times catch people when they are most active.
Adapting Strategies From Failures
Not all attempts are successful. Learning from mistakes can also guide us.
- Company D: Sent emails on Mondays at 8 AM. Low open rates.
- Company E: Tried Fridays at 4 PM. High bounce rates.
- Company F: Used weekends. Very poor engagement.
These companies learned that early mornings and weekends are not ideal. People are often busy or not checking emails then.
Analyzing both successes and failures helps refine your strategy. Try different times, track results, and adjust as needed.
Conclusion: Synthesizing Timing Strategies
Choosing the best time to send cold emails can be tricky. Timing plays a vital role in improving open rates and responses. We’ve explored various factors that affect the timing of your emails. Now, let’s bring it all together and apply these insights.
Key Takeaways
- Emails sent on Tuesday and Thursday perform better.
- Morning emails between 8 AM and 10 AM get more attention.
- Emails sent at 1 PM to 3 PM see higher engagement.
- Consider the recipient’s time zone for better results.
Implementing Insights For Success
Use these strategies to optimize your cold email timing:
- Schedule emails for Tuesday and Thursday.
- Send emails between 8 AM and 10 AM or 1 PM to 3 PM.
- Adjust sending time based on the recipient’s time zone.
- Test different times to find what works best for your audience.
| Day | Optimal Time | Engagement Level |
|---|---|---|
| Tuesday | 8 AM – 10 AM | High |
| Thursday | 1 PM – 3 PM | High |
| Wednesday | 8 AM – 10 AM | Moderate |
By following these tips, you can improve your cold email results. Always track your performance and adjust your strategy as needed.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Best Time Of Day To Send Prospecting Emails?
The best time to send prospecting emails is between 10 AM and 11 AM. Aim for mid-week, especially Tuesday to Thursday.
Should I Send A Cold Email On Friday?
Sending a cold email on Friday can be risky. People may overlook it as they prepare for the weekend. Aim for mid-week instead.
Is Monday A Good Day To Cold Email?
Yes, Monday is a good day to cold email. People often check emails to plan their week.
What Is The Best Time To Send An Email Response?
The best time to send an email response is between 10 AM and 11 AM. Emails sent during this period have higher open rates. Early afternoon, around 1 PM to 2 PM, is also effective. Avoid late evenings and weekends for optimal engagement.
Conclusion
Choosing the right time to send cold emails can boost your response rates. Test different times and track results. Early mornings or mid-week often work best. Consistency is key to finding what works for your audience. Fine-tuning your approach will lead to better engagement and success.